모 양갈래를 좋아하는 디코 서버에서 방학 기간동안 매일 3문제씩 골5,4 랜디를 하자! 라는 계획을 서버장이 추진하게 되어서 시작했습니다. 할때마다 블로그에 정리하려 하는데 매일 쓰다보면 풀이 퀄리티가 떨어지는 날도 있을수 있으니 더 궁금하면 댓글로 달아주세요.
[A] 유닛 이동시키기 boj - 2194번
정직하게 2차원 격자에서의 BFS를 구현해주면 됩니다. 다만 주의할점은 격자를 벗어났는지 벗어나지 않았는지 판정할때 움직이는 점의 크기가 a x b 크기이기 때문에 경계를 계산할때 조금 조심해줘야 합니다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define PRECISION 0
#define fr first
#define sc second
using ll = long long;
using ld = long double;
typedef pair<ll,ll> pll;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
const ll MOD = 1e9+7;
int n, m, a, b, k;
int grid[505][505];
int dx[4] = {1,-1,0,0};
int dy[4] = {0,0,1,-1};
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.setf(ios::fixed); cout.precision(PRECISION);
cin >> n >> m >> a >> b >> k;
while(k--){
int row, col;
cin >> row >> col;
grid[row][col] = -1;
}
int strow, stcol;
int enrow, encol;
cin >> strow >> stcol;
cin >> enrow >> encol;
grid[strow][stcol] = 1;
queue<pii>q;
q.push({strow, stcol});
while(!q.empty()){
int currow = q.front().fr;
int curcol = q.front().sc;
//cout << currow << ' ' << curcol << endl;
if(currow==enrow && curcol == encol) break;
q.pop();
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
int nrow = currow + dx[i];
int ncol = curcol + dy[i];
if(nrow<=0 || nrow+a-1>n || ncol<=0 || ncol+b-1>m) continue;
bool obstacle = false;
for(int j=0; j<a; j++){
for(int k=0; k<b; k++){
if(nrow+j<=n && ncol+k<=m){
if(grid[nrow+j][ncol+k]==-1){
obstacle = true;
}
}
}
}
if(obstacle) continue;
if(grid[nrow][ncol]) continue;
grid[nrow][ncol] = grid[currow][curcol] + 1;
q.push({nrow, ncol});
}
}
if(grid[enrow][encol]>0) cout << grid[enrow][encol] - 1;
else cout << -1;
}[B] - 최장 최장 증가 부분 수열 boj - 25343번
"왼쪽 위 칸에서 가장 오른쪽 아래 칸까지 최단 경로로 이동하려고 한다." 라는 조건으로 인해 칸 사이에서 움직일때 왼쪽이나 위쪽으로는 갈수 없습니다.
따라서 일반적인 LIS의 점화식을 2차원으로 확장시켜주면 그대로 적용시킬수 있는데 다음과 같이 확장할수 있습니다.
dp[k][l] = dp[i][j] + 1 (i < k, j < l) (arr[i][j] < arr[k][l])
따라서 4중 for문을 사용하고 시간복잡도는 O(N^4) 가 되지만 N제한이 100밖에 되지 않아 넉넉히 통과합니다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, ans=1;
int dp[105][105];
int arr[105][105];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
cin >> arr[i][j];
dp[i][j] = 1;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
for(int k=i; k<n; k++){
for(int l=j; l<n; l++){
if(arr[k][l]>arr[i][j]){
dp[k][l] = max(dp[k][l],dp[i][j]+1);
ans = max(ans, dp[k][l]);
}
}
}
}
}
cout << ans;
}[C] - 균형 boj - 22968번
아니 왜 자료구조 중간고사가 여기서 또 나와...
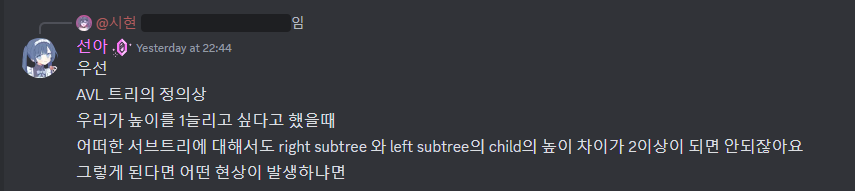
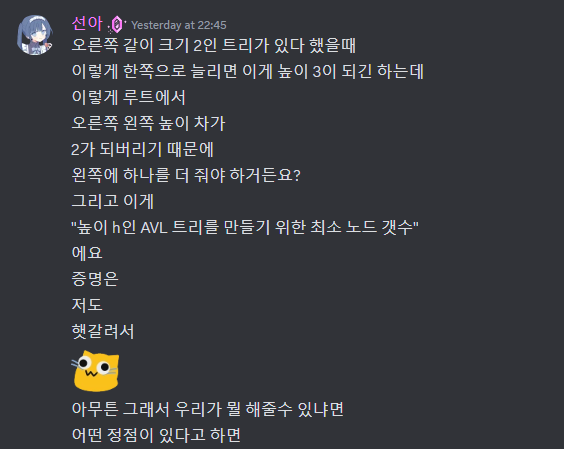
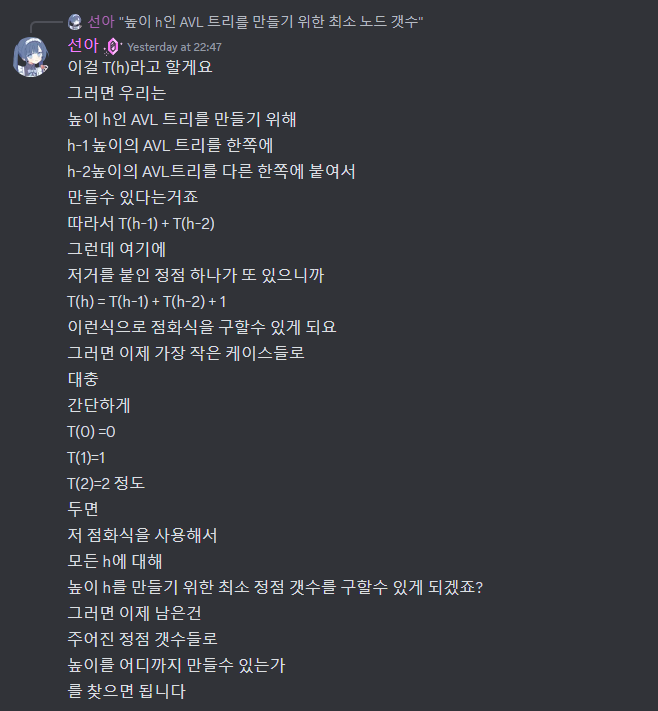
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define PRECISION 0
#define fr first
#define sc second
using ll = long long;
using ld = long double;
typedef pair<ll,ll> pll;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
const ll MOD = 1e9+7;
int n, m, a, b, k;
int t;
ll dp[50]={0, 1};
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.setf(ios::fixed); cout.precision(PRECISION);
for(int i=2; i<=45; i++){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2] + 1;
}
cin >> t;
while(t--){
ll v;
cin >> v;
if(binary_search(dp+1, dp+44, v)) cout << lower_bound(dp+1, dp+44, v)-dp << endl;
else{
cout << lower_bound(dp+1, dp+44, v)-dp-1 << endl;
}
}
}'PS > BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| /<30326> Heap Structure - TOPC 2023 (0) | 2024.06.24 |
|---|---|
| 2023.06.24 골랜디 (0) | 2023.06.24 |
